
My family eats rice daily, and we often argue about which type of rice is better for our health. We’ve come with two options: brown rice vs. white rice.
How is the difference between brown rice and white rice?
Is switching to brown rice lead to diet effects and weight loss?
Also, which rice is better in certain situations?
Let’s put a clear understanding between these two types of rice and choose which rice you’ll need from today’s forward.
 Content List
Content List
- Difference Between Brown Rice and White Rice
- Brown Rice vs White Rice: The Structure
- Brown Rice vs White Rice: Calories and Carbohydrate Content
- Brown Rice vs White Rice: Nutritional Differences
- Summary: Difference between Brown Rice and White Rice
- Is Changing to Brown Rice Effective for Diet?
- Better Rice Choice for Diet: Koso Genmai
- Which rice is better for you?
- Brown Rice vs. Brown White Q&A
- Bottom Line: Why is Brown Rice Healthier?
- Recommended Products for Brown Rice
Difference Between Brown Rice and White Rice
Brown rice and white rice came from the same rice plant. What makes it different is the grain processing method before it reaches our hands. These points below are the difference between brown rice vs. white rice:
Brown Rice vs White Rice: The Structure
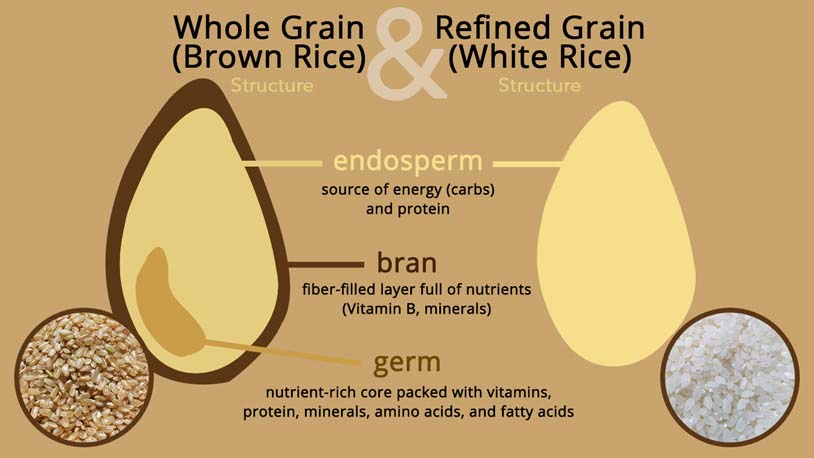
As you can see, brown rice is a whole grain consist of rice bran, endosperm, and germ with only the husk (the inedible outermost layer of grain) removed.
Brown rice is packed with rice bran, a layer rich in fiber and nutrients (such as B vitamins, proteins and minerals), the carbs concentrated rice endosperm, and the nutrient-rich rice germ. This structure makes brown rice has a yellowish to brown color. The fiber-filled bran makes brown rice has a nutty, earthy taste close to black rice.
White rice, on the other hand, is a refined grain which only has the endosperm left. The milling process removes the rice husk, bran, and germ and thus makes it has a bright to shiny white color. The rice endosperm makes white rice stickier and starchier. The taste is milder and softer, with a hint of sweetness because of the starch. Some white rice products are enriched to balance the vitamins and nutrients like brown rice.
Difference 1: Structure differences in brown rice vs. white rice lead to differences in nutritional content, color, taste, and texture.
Brown Rice vs White Rice: Calories and Carbohydrate Content
If compared with white rice, brown rice has the image to have low calories.
How is it actually?

Let’s learn what is calorie and carbohydrate before comparing their amount.
Calorie:
Calorie is a unit of energy.
It is referring to the energy we got from eating food and the energy used to carry out activities.
Carbohydrate:
It is a nutritional component, the main source of energy for the body.
Formed when combined with dietary fiber.
Next, we investigated the difference in calories and carbs between brown rice and white rice.
| Content | Cooked Brown Rice (100 g) | Cooked White Rice (100 g) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 112 Kcal | 130 Kcal |
| Carbohydrate | 53.4 g | 55.5 g |
These small differences in calories and carbohydrates, however, is significant for those who consume rice daily. Let’s also consider this factor when choosing rice!
Difference 2: There was not much difference in the number of calories and carbohydrates in brown rice vs. white rice.
However, this factor could be significant if you consume rice daily.
Brown Rice vs White Rice: Nutritional Differences
Brown rice has superior nutritional facts than white rice. Let’s discuss the most significant nutrition one by one.
| Nutrition | Cooked Brown Rice (100 g) | Cooked White Rice (100 g) |
|---|---|---|
|
Fiber To relieve constipation, lowers cholesterol levels, control blood sugar levels, and help to maintain a healthy weight. |
2.1 g | 0.4 g |
|
Protein Important for repairing and growing cells. Good for dieting because it can lower hunger hormone. |
4.2 g | 3.8 g |
|
Lipid Rice’s lipid consist of healthy unsaturated fatty acids to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. |
1.5 g | 0.5 g |
|
Vitamin B1 Helps body cells convert food into energy, relieve fatigue, and promote sugar metabolism. |
0.24 mg | 0.03 mg |
|
Potassium Mineral that functions to regulate blood pressure, prevent stroke, osteoporosis, and kidney stones. (*the exception for those with kidney disease) |
143 mg | 44.3 mg |
|
Magnesium Mineral to relieve constipation, promote sugar metabolism and help prevent diseases like osteoporosis, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and stroke. |
74 mg | 10.4 mg |
* The table represents the comparison between 100gr brown rice and 100gr white rice.
* Source: Nihon Shokuhin Hyoujun Seibunhyou 2015-nenban (Standard Diagrams of Japanese Food Composition 2015 7th edition)
* Book Source: Doku Dashi Koso Genmai Daietto (Brown Rice Detox Diet) by Okamoto Uka
Note: Please use this information for reference. Each manufacturer has its own nutritional value.
Difference 3: Brown rice contains a greater level of nutrients such as fiber, protein, lipid, vitamin B1, potassium, and magnesium than white rice.
Summary: Difference between Brown Rice and White Rice
We’ve summarized and compared the reasons why brown rice is superior to white rice.
-

BROWN RICE
● Brown rice’s structure consist of grain consist of rice bran, endosperm, and germ
● The whole grain that naturally has higher nutrition, rarely enriched and fortified
● 100g of cooked brown rice has 112 Kcal and 53.4 g carbohydrates.
● 4-5x higher in fiber content
● Higher in protein content
● Higher in lipid content
● Higher in Vitamin B1, B2 content
● Higher in minerals (potassium, magnesium)
● Higher in antioxidant content
● Lower Glycemic Index level (average GI of 68)
● Shorter shelf life (6 months)
-

WHITE RICE
● White rice’s structure only has the endosperm left due to the milling process
● The refined grain that sometimes enriched and fortified with vitamins and minerals
● 100g of cooked white rice has 130 Kcal and 55.5 g carbohydrates.
● Lower fiber content
● Lower protein content
● Lower lipid content
● Lower in Vitamin B1, B2 content
● Lower in minerals (potassium, magnesium)
● Lower in antioxidant content
● Higher Glycemic Index level (average GI of 73)
● Longer shelf life (1 year)
The differences above showed that brown rice is preferable in a lot of aspects. But is changing to brown rice effective for diet? And what kind of rice is recommended for certain conditions? Continue reading to find the answer!



Is Changing to Brown Rice Effective for Diet?

The most important thing to note about controlling weight when dieting is how easily your blood sugar rises after a meal, or consuming the low GI (Glycemic Index) food.
Brown rice, which is rich in dietary fiber, can moderate the blood sugar level after a meal. You’ll feel fuller over a longer time, too, which could prevent you from eating additional snacks.
According to a study, brown rice is also abundant with a promising anti-obesity component called γ‐Oryzanol. Consuming brown rice could prevent the risk of obesity.
For those who want to achieve weight loss or maintaining healthy body weight in diet,
Brown rice is said to be an effective food for dieting rather than only having a slight difference in calories than white rice.
Better Rice Choice for Diet: Koso Genmai
For those who are still highly concerned about calories and carbs for dieting, we recommend you to try Koso Genmai.
Koso Genmai or Enzyme/Fermented Brown Rice is a cooked sprouted brown rice with Azuki beans (red beans) and salt, then fermenting or keeping it warm for 2 to 3 days. Koso Genmai is packed with GABA and superior nutrients if compared with normal brown rice. Also, Koso Genmai is chewier and has more umami. It’s a delicious dish to consume even if you are on a diet.
Watch our video below for a simple explanation in making Koso Genmai.
We also have a detailed article about how to make Koso Genmai. Please try it by all means!

Which rice is better for you?

In certain cases, one type of rice may be preferable to another. This section will help you consider which rice is better for certain people with certain conditions or diet goals.
High Fiber Diet
People who got recommendation from their doctor to have a high fiber diet might consider to choose brown rice than white rice.
Brown rice is suitable for the high fiber diet because it is high in fiber, high in Vitamin B, high in Magnesium, abundant with γ‐Oryzanol, and has a low GI (Glycemic Index).
Consider to choose brown rice if you want to reduce the risk of:
• Stroke
• Obesity
• Heart disease
• Type 2 diabetes
• High cholesterol level
• High blood pressure
• Constipation
Low Fiber Diet
On the other hand, people who are doing the low fiber diet will consider eating white rice than brown rice.
White rice contains less fiber than brown rice, so it is recommended for those who have diverticulitis, people before or after bowel surgery, inflammatory bowel disease, colorectal cancer, and diarrhea.
Kidney Disease
People with kidney disease are advised to limit potassium intake in their diet (below 2000 mg per day).
Excess potassium cannot be processed right away for people with kidney disease and will remain in the blood. If the potassium level becomes too high for these people, it may cause other health concerns such as heart attacks.
Brown rice has more potassium and phosphorus than white rice.
Thus, white rice will be better than brown rice in this case.
Athletes
Athletes or people with high physical activity need adding more carbohydrates to their diet to help fuel workouts and facilitate recovery. Carbs also replenish muscle glycogen after workouts.
Consuming starchy, easy to digest carbs like white rice is preferable for pre and post-working meals. Thus, white rice is considered a safe carbohydrate approved in sports nutrient recommendation for athletes to achieve their goals.
On the contrary, white rice may not be the best choice for people with a sedentary lifestyle or desk-bound lifestyle.
Macrobiotic Diet
“I want to eat healthier, lose some extra weight, and prevent health problems with macrobiotic diet!”
We would like to recommend eating brown rice for people who are working hard with macrobiotic diet by all means.
Unlike white rice, brown rice is superior in nutrients and can make up the required energy for the day without having to overeat. Whole grain like brown rice is heavily emphasized in this diet. For more information about macrobiotic diet, please refer to this article:

Brown Rice vs. Brown White Q&A
- Brown rice vs. white rice: which one is healthier?
- In overall aspects, brown rice is considered healthier than white rice.
Brown rice has the bran and germ part of the grain, which is the source of its nutrition. Meanwhile, white rice is milled and polished without the bran and germ part.
- Is switching to brown rice good for weight loss?
- Yes. Brown rice is rich in dietary fiber and low GI that can moderate the blood sugar level after a meal. On the contrary, eating food that is easier to increase blood sugar levels can make it easier to gain weight.
You’ll feel fuller over a longer time because brown rice is harder to digest, too.
- What is the recommended rice if I want to gain weight and build muscles?
- White rice is suitable for gaining weight because it’s more digestible and tends to raise blood sugar levels after a meal.
However, brown rice is suitable for building muscles because it is rich in protein.
You can choose white rice and add additional proteins from other food sources. In case you want to choose brown rice to take the other nutrients, make sure to cook it in a soft texture, so it’s more digestible.
- What are the certain conditions recommended to consume white rice rather than brown rice?
- ● People doing low fiber diet
● Poeple with kidney disease
● People with high physical activity or athletes
- What is the shelf life of brown rice vs. white rice?
- Because of the oil in its bran layer, uncooked brown rice has a shorter shelf life than uncooked white rice.
The uncooked brown rice could last up to 6 months in a cool place, while uncooked white rice could last up to 1 year. Please store both rice in a closed container.
- I heard that brown rice is healthier than white rice. Is brown rice has any disadvantage compared to white rice?
- Brown rice contains more arsenic than white rice. It is a metal element naturally present in rice and could be toxic for continuous long-term consumption. However, we can reduce arsenic content by wash the rice and soak it overnight.
This fact makes it takes more time to cook and enjoy the delicious brown rice compared to white rice.
- I want to know how to cook brown rice. Any tips?
- Please check out our article “How to Deliciously Cook Brown Rice (3 Ways)”. This article will tell you the steps and tips to cook brown rice.
Bottom Line: Why is Brown Rice Healthier?
White rice is not completely unhealthy. It is just losing a few essential nutrients than brown rice. White rice may not be a good option for those with high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, stroke, obesity, heart disease, and constipation.
If you are consuming rice on daily basis, you may want to replace it with brown rice. Brown rice is considered to be more nutritious for you to maintain a healthy weight and lifestyle with all the nutrients contained.
Please note that several conditions recommend white rice over brown rice.
Want to challenge into something even greater? Go for Koso Genmai (Enzyme/Fermented Brown Rice). You can get the utmost nutrients from this dish with just a little more effort.
Try making sprouted brown rice on your first try and upgrade yourself even further by making Koso Genmai.

Recommended Products for Brown Rice
If you want to eat brown rice as fast as possible, kindly check Kawashima-ya’s original Koso Genmai retort pouch.











