
There are various types of bacteria in your digestive system, either the good bacteria, or bad bacteria. Your overall health can be impacted by the bacteria in your gut. When your gut is not healthy, your overall health would become disturbed or unbalanced. It could impact your mood as well. Find out more in this article about what can you do to keep your gut healthy and clean.
What is Gut Health??
Gut health is the condition where you have a good balance of bacteria in your gut. Many people misunderstand that the bad bacteria in your gut should be gotten rid off. But Actually the important thing is to maintain the balance between the good bacteria and the bad bacteria.
Scientists have learned that the microbes and bacteria living in your gut can have a positive or negative impact on your digestive, immune, your skin, your brain, and even your mental health. However people with a wide variety of good bacteria in their gut tend to be healthier. And a healthy gut includes a variety of prebiotic and probiotic organisms.
3 Types of Bacteria in Your Gut
There are three types of bacteria based on their action in your gut; beneficial (good) bacteria, harmful (bad) bacteria, and opportunistic bacteria. Good bacteria is bacteria that is necessary and does a good job for your body. It plays an important role to maintain health, prevent disease, and anti-aging. Examples of good bacteria are bifidobacteria and lactic acid bacteria.
On the other hand, bad bacteria have negative effects on the body. It produces harmful substances for your body. Examples of bad bacteria in your gut are Clostridium perfringens, Staphylococcus, and Escherichia coli (E. coli; toxic strain). They inhibit health by triggering disease and make aging faster. However, some of bad bacteria produce necessary nutrients and attack other pathogens in your gut, so it cannot be said that they are all bad.
Opportunistic bacteria cause no trouble when you are healthy, but when your body is weak, it could have negative effects to your intestines . Examples of opportunistic bacteria are Bacteroidetes, E. coli (nontoxic strain), and Streptococcus.
Based on our interview with Shinichiro Otake, Director of Otake Gastroenterology Clinic, Japan, the optimal balance of those three bacteria types is said to be; 20% for good bacteria, 10% for bad bacteria, and 70% for opportunistic bacteria.
Why is it important to keep your gut healthy?

Your gut has an important role. Some researches found that gut have such a strong connection with so many other elements of our wellbeing, especially physical wellbeing and mental wellbeing. That’s why it’s important to keep it healthy. Some of gut primary function include;
1. To absorb water, minerals, vitamins, electrolytes, and other nutrients from the food material we have digested for your entire body.
2. The main organ that receives metabolic waste, toxins, and microorganisms that cause illness from the circulatory system and eliminate them.
3. Good bacteria in an unhealthy gut will produce short-chain fatty acids. This short-chain fatty acid can help to relieve stress, stabilize your mental health, and improve your skin tone.
4. Gut is where most of the serotonin, a hormone that makes us feel happy, is produced. Food cravings and emotional eating often originate from this connection.
Signs of Unhealthy Gut

Nowadays, people life tends to have high stress levels. Many of us having too little sleep, and eating processed and high-sugar foods in daily basis. This may affect other aspects of your health, such as your brain, heart, immune system, skin, weight, hormone levels, ability to absorb nutrients, even the development of cancer. Here are the most common signs of an unhealthy gut.
#1 Stomach discomfort

If you regularly feeling discomfort in your stomach like gas, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and heartburn, it might be the signs of an unhealthy gut. A review published in July 2018 in the journal F1000 Research mentioned that imbalances in the gut bacteria, called dysbiosis, can play a role in the development of Irritable bowel syndrome for some people.
#2 Food Cravings

Research published in August 2014 in the journal Bioessays suggested that bacteria in your gut are possible to manipulate host eating behavior to increase their fitness, sometimes at the expense of host fitness. Bacteria may do this through two potential strategies; generating cravings for foods that they specialize on or foods that suppress their competitors, or inducing dysphoria until you eat foods that enhance their fitness.
#3 Unintentional weight changes
Research has found differences in the gut bacteria of lean and obese people. A study published in July 2016 in the journal Nutrition Today proved that the gut bacteria is intrinsically linked with overall health, including obesity risk. Obesity and obesity-related metabolic disorders are characterized by specific alterations in the composition and function of the human gut bacteria.
#4 Constant Fatigue and Sleep Disorders

A study published in April 2017 in the journal Microbiome stated that people with chronic fatigue syndrome may have imbalances in their gut microbiome, which consists of the bacteria, microorganisms, fungi, and viruses present in the gastrointestinal tract.
#5 Skin Irritation

Research has shown a link between an unhealthy gut and skin problems such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis. Skin conditions like eczema may be related to a damaged gut because leaking of certain proteins out into the body, which can in turn irritate the skin.
A review published in July 2018 in the journal Frontiers in Microbiology stated that the influence of the gut microbiome extends to involve distant organ systems including the skin. With intentional modulation of the microbiome, probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics have proven beneficial in the prevention and/or treatment of inflammatory skin diseases including acne vulgaris and psoriasis.
Reference:
The Gut Microbiome as a Major Regulator of the Gut-Skin Axis
#6 Mood issues and Focus Difficulty

There is a well-documented link between the gut and the brain, and the influence of the gut may also extend to your mood. A review published in September 2017 in the journal Clinics and Practice found that dysbiosis and inflammation of the gut have been linked to causing several mental illnesses including anxiety and depression, which are prevalent in society today.
Also, Dr Datis Kharrazian in his book “Why Isn’t My Brain Working?” says that inflammation in the brain slows down conductivity between neurons. It slow your brain and triggers slow, dull thinking, make you difficult to focus and tends to suffer from brain fog.
Reference:
1) Gut Microbiota’s Effect on Mental Health: The Gut-Brain Axis
2) Why isn’t my brain working
How to Improve Your Gut Health

Rather than doing a short term diet methode or extreme gut cleansing, the healthiest way to do is change your lifestyle. Since gut health include so many aspect of well-being, here are our tips to improve your gut health:
Take probiotics and eat fermented foods

Talking about gut health, probiotic is one of the most popular topic regarding gut nutrition. Probiotics are living good bacteria. There are many probiotic foods that naturally contain good bacteria such as yoghurt. You can also consider supplement such as Lactic Acid Bacteria Powder.
However, probiotic supplements and foods is not recommended for people with weakened immune systems or serious illnesses. As with all nutritional supplements, probiotics should be taken according to the directions and with the guidance of a physician or health care provider.
Another great option is fermented foods, as they contain beneficial bacteria that thrive on the naturally occurring sugar or fiber in the food. You can buy your favorite fermented food, or try to make them by yourself using fermenting bacteria. There is also a product from Japan, koji, which usually use as ingredients to make Japanese fermented food, such as miso, shoyu, mirin, sake, etc. Here is our recommendation for your reference;
| Type | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Fermented foods | Helps to grow good bacteria in your gut | Yogurt, cheese, amazake, miso, kimchi, natto, Apple Cider Vinegar, etc. |
| Probiotics Supplements | As support to get more probiotics other than from foods | Lactic Acid Bacteria, whether in powder, pills, or capsule form |
Eat Prebiotic Fiber
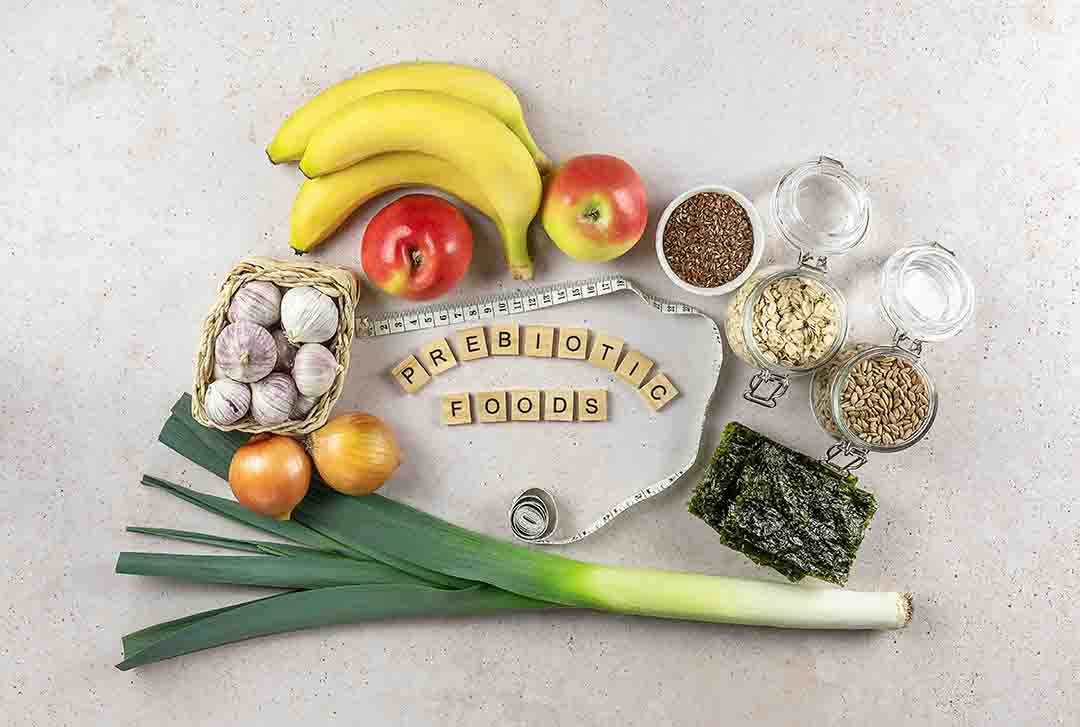

Another popular topic regarding gut nutrition is prebiotics. Even though Probiotics and Prebiotics sound familiar, they have different role for your gut health. Prebiotics are food for the good bacteria in your gut that you could get from types of carbs and mostly fiber. Since humans can’t digest them, the good bacteria in your gut eat this fiber. Prebiotics can be found in vegetables, fruits, oats, etc. Here is our summary about prebiotics for your reference;
| Type | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Prebiotics Fiber | Cleans your gut and feeds on gut bacteria (probiotics) | Burdock, wakame seaweed, mushrooms, garlic, asparagus, banana, oats, barley, etc. |
Get Enough Sleep
Not getting enough of sleep can have serious side-effects on your gut health, which can contribute to more sleep issues if you don’t work on it. Try to prioritize getting at least 7–8 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night. If you have trouble sleeping, you might want to consult to doctor.
A 2014 research indicated that irregular sleep habits and disturbed sleep can have negative outcomes for the gut bacteria composition, which may increase the risk of inflammatory conditions.
Reference:
Circadian Disorganization Alters Intestinal Microbiota
Exercise Regularly
Exercising regularly contributes to good heart health and weight loss or weight maintenance. A research in 2014 suggested that it may also improve gut health, which in turn help to control obesity. The research also found that athletes had a larger variety of gut bacteria than non-athletes.
Reference:
Exercise and associated dietary extremes impact on gut microbial diversity
Manage Stress
Managing stress is important for many health aspects, including gut health. A research stated that psychological stressors such as psychological stress, environmental stress, and sleep deprivation can negatively affect the bacteria in your gut, even if the stress is only for short-term period.
Some stress management techniques include meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation.
What to avoid for an healthy gut?
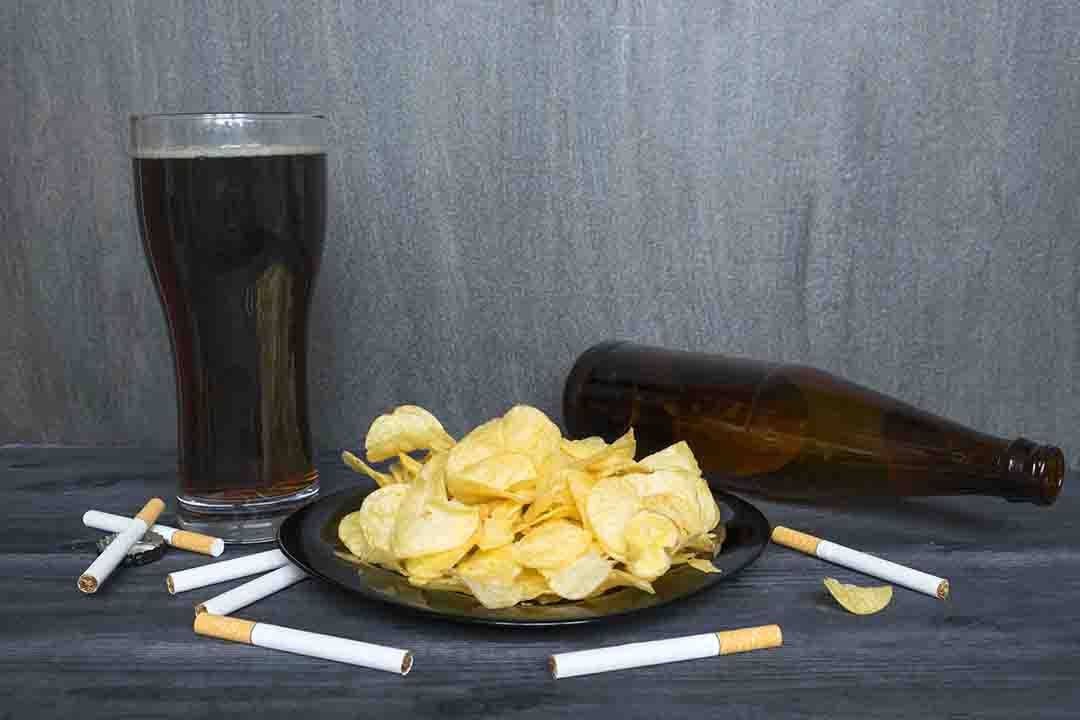

Food That You Should Avoid
Food is the most important thing to consider related to gut health since what you eat directly influences the composition of bacteria in your gut, which in turn impacts your health. To keep your gut healthy, it is best to avoid high-sugar foods, junk foods, fried foods, too spicy foods, etc. It is also important to keep your diet balance. remember that too much of anything is bad for you.
Avoid Smoking
Studies suggest that the composition of gut bacteria is altered due to smoking. Smoking increase potentially harmful bacteria and decreasing the levels of beneficial ones.This interaction may contribute to the development of intestinal and systemic diseases, particularly inflammatory bowel diseases.
Reduce Your Alcohol Intake
Drinking too much may negatively affect your gut bacteria composition. Repeated alcohol use can cause gastritis, an irritation of the gut in which it becomes inflamed. Such inflammation can lead to heartburn, chronic discomfort, ulcers and bacterial infections.
FAQ about Gut Health
- What is gut health?
- Gut health is the condition where you have a good balance of bacteria in your gut. The optimal balance of the bacteria types is said to be; 20% for good bacteria, 10% for bad bacteria, and 70% for opportunistic bacteria.
- Why is Gut Health important?
- Gut health is important because your gut have an important such as to absorb water, minerals, vitamins, electrolytes from the food material you have digested. Gut is also the main organ of elimination which receives metabolic waste and toxins from the circulatory system and eliminate them. It is also known that intestinal and gut health is very related to the skin, mental health, and any other aspect of your well-being.
- What is gut cleanse and is it necessary?
- Gut cleanse is claimed to be one of many ways to improve gut health. Generally, gut cleansing refers to colonic irrigation or hydrotherapy. However self-administered cleanses parctice such as juice or tea detox, colon cleanse pills, and enemas are now a trending although the safety and necessity of these are often called into question. In fact, an healthy person wouldn’t need gut cleansing with extreme methods because your body has its own ways of keeping itself clean on the inside.
- What are the signs if I have Unhealthy Gut?
- Most common signs of an unhealthy gut are; stomach discomfort, intense food cravings, unintentional weight changes, constant fatigue and sleep disorders, skin irritation, mood and focus issues. For the detail please refer to Unhealthy gut session in this article.
- How do I Improve my Gut Health?
- Not only food, there are a lot of aspect to fix if you want your gut to be healthy. You should consume food which contains a sufficient amount of probiotics and prebiotics, get enough and high quality sleep, exercise regularly, etc. For further explanation please read our tips to improve gut health in this article above.
- How gut health related to wellbeing?
- When your gut is healthy and works as it should be, good bacteria will produce short-chain fatty acids that can help to relieve stress, stabilize your mental health, and improves your skin tone. Gut balance also known to have a profound effect on your brain since more than 90 percent of the serotonin is produced in the gut. Gut bacteria imbalance can also cause food cravings and emotional eating.
- What to avoid to have a healthy gut?
- For an healthy gut you need to avoid too much alcohol intake, smoking, and unhealthy foods such as high-sugar foods, junk foods, fried foods, too spicy foods, etc. Remember to balance your diet. Too much of anything is bad for you.
Product Recommendation to Improve Gut Health


 Content List
Content List









